The Performance Accountability Council released its quarterly progress report on the government’s Trusted Workforce 2.0 clearance reform efforts. The report notes improvements in some key areas, including a downward trend for Top Secret security clearance processing times, and newly updated metrics around preliminary security clearance determinations. Delays in implementation of the National Background Investigation Services (NBIS) were noted in the previous report, and the latest update notes that progress is being made toward updating the framework, which will include pushing out some deadlines for implementation of things like the 3-tier framework.
With ongoing pressure around security clearance processing times, the PAC recently began updating with a new metric – preliminary decisions, indicating those onboarded with interim clearance eligibility meaning they’re not waiting the full 87 or 155 day averages for final clearance determinations. In contrast, preliminary determinations were made within a month, on average, for federal applicants, and for under a week for DoD/industry applicants.
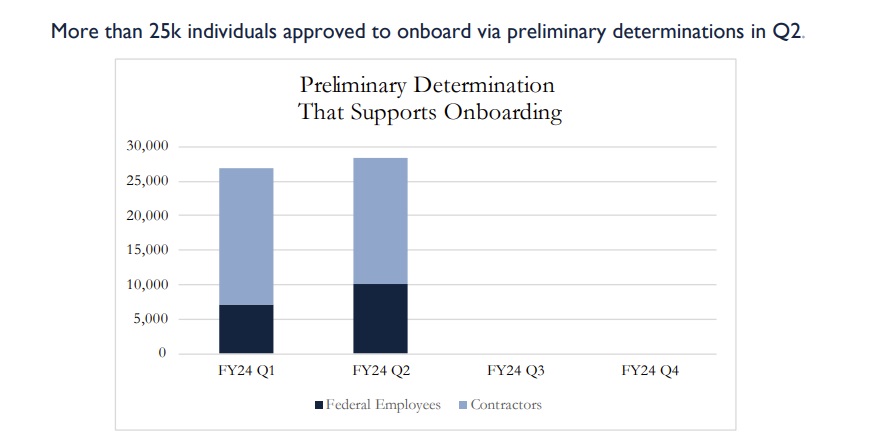
The new metrics around preliminary onboarding determinations are designed to note the ongoing efforts to reduce friction created by security clearance determinations in the overall national security hiring process. Current metrics include just figures released by the Department of Homeland Security and Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency (DCSA).
“As described in the quarterly update, this year brings a focus on the concept of a ‘determination that supports onboarding.’ This performance metric focuses on the average time it takes for personnel vetting to approve an individual to come to work to support critical missions,” a DCSA spokesperson responded when asked about the new preliminary onboarding metrics. “It shifts the focus away from pure end-to-end timeliness that does not consider that many individuals can come on board after robust initial checks and a preliminary determination.”
CV Alerts and Overall Clearance Marketplace
The number of Continuous Vetting (CV) alerts continues to increase as more individuals are enrolled in CV programs. DCSA processed approximately 15,000 more alerts in the second quarter of fiscal year 2024, due to both new enrollments into CV along with increased self-reporting and adverse information reporting on the part of security officers. Conveying the importance of self-reporting even as CV is implemented remains a priority, and questions about what information needs to be self-reported continue to be some of the top questions asked by applicants, according to soon to be released results from the ClearanceJobs 2024 State of the Facility Security Officer Survey.
When it comes to the overall size of the national security population, with approximately 5.2 million individuals eligible for access today. The total in-access number dropped slightly in the second quarter of fiscal year 2024, with a 3% reduction from FY 2013, and at 2.4 million individuals.
A number of additional milestones, including the incorporation of the new security clearance application, the Personnel Vetting Questionnaire (PVQ) into eApp, transition to Trusted Workforce 1.5 CV operations, and enrollment of the full national security population including low risk positions into CV will be updated based on NBIS recovery timelines and progress.




